Cache Monitoring
¶
PHP
The Monitoring Dashboard provides an overview of the caches usage and hit-rate evolution over time for PHP applications:
- APCu Hit Rate
- APCu Usage
- OPcache Hit Rate
- OPcache Usage
- OPcache Interned Strings Buffer Usage
- PCRE Usage
- RealPath Usage
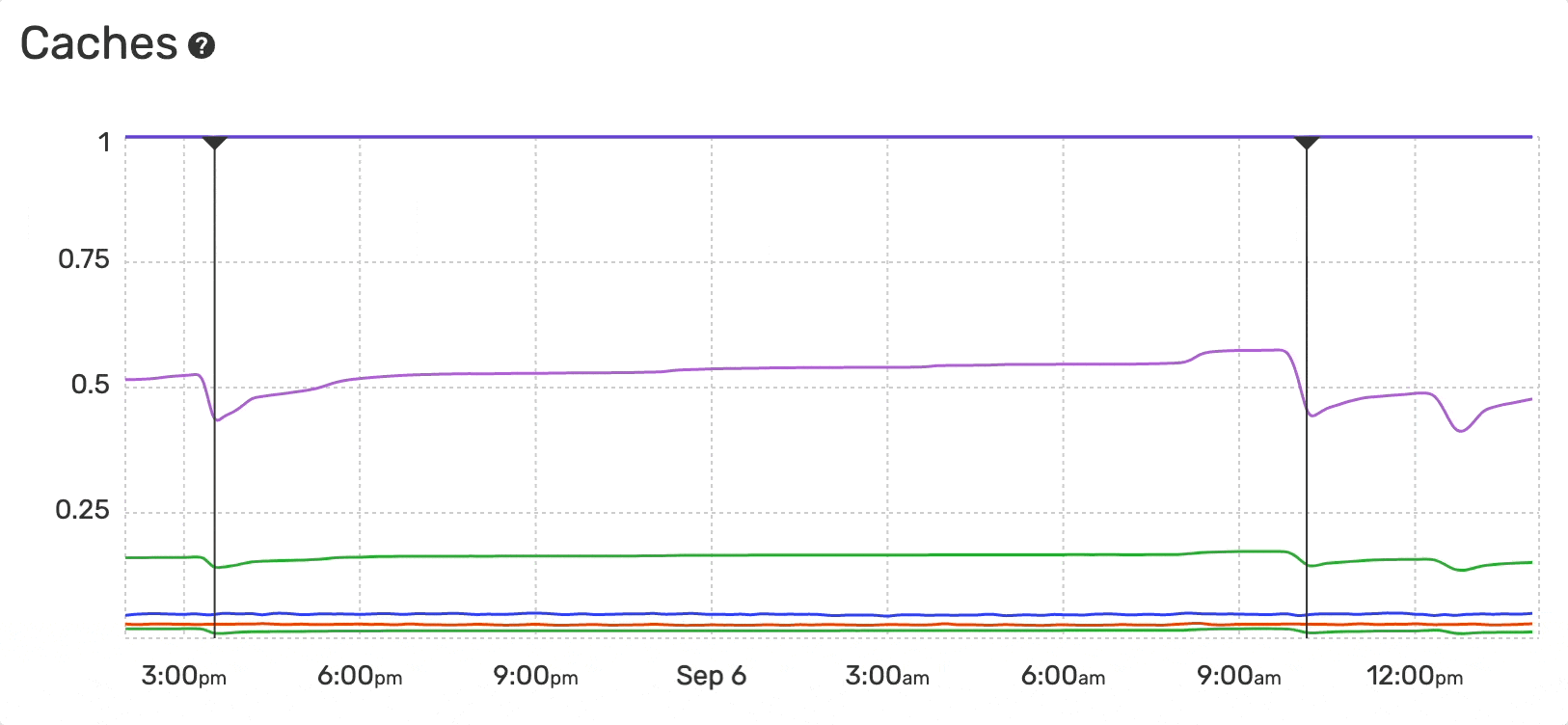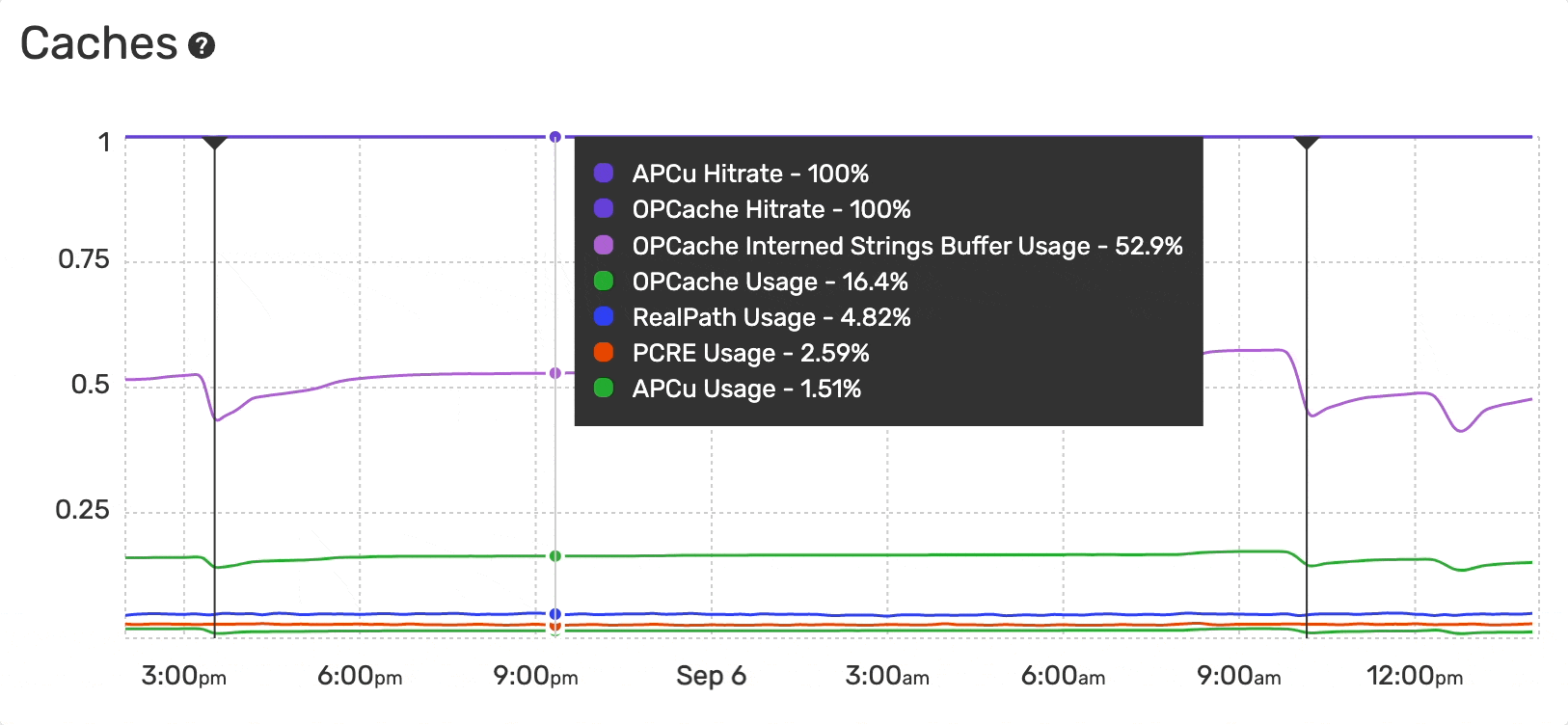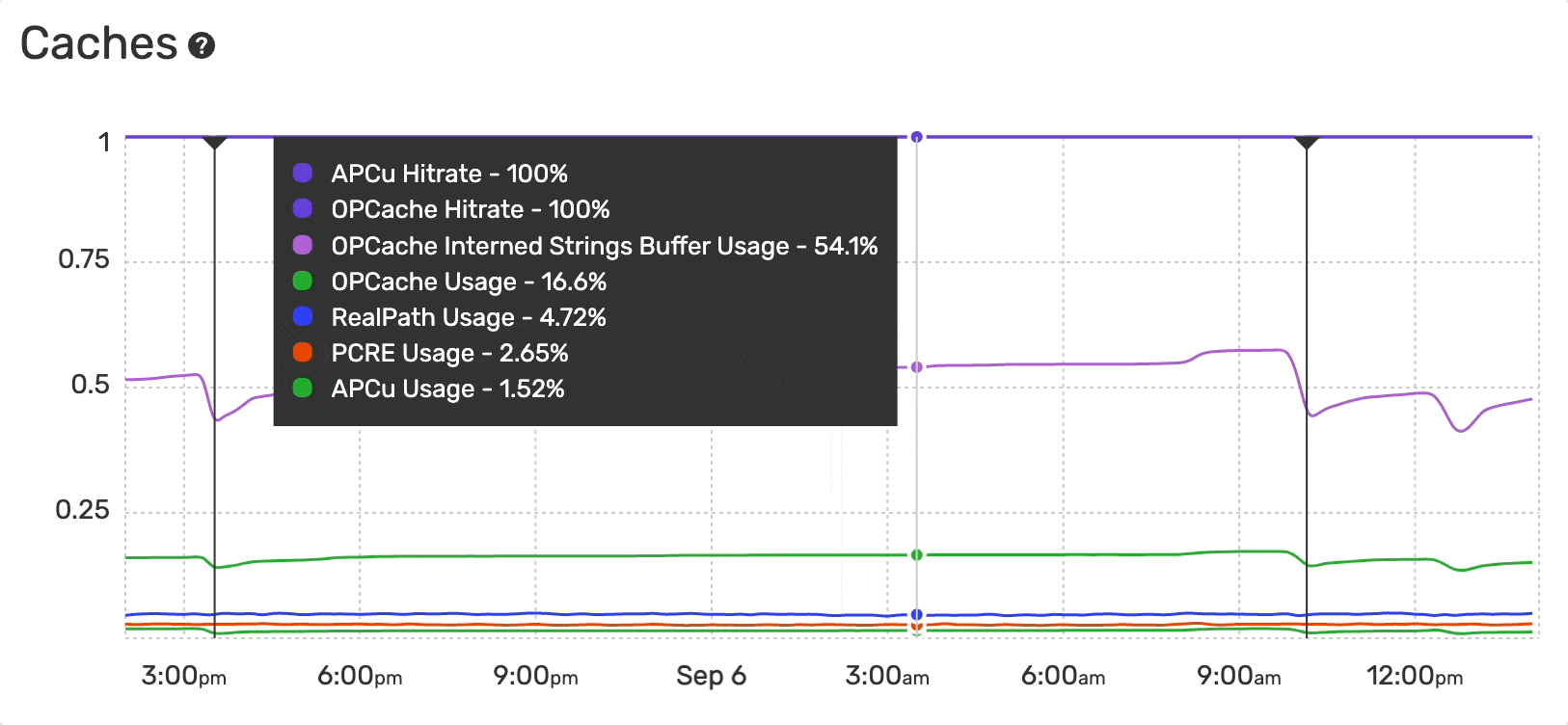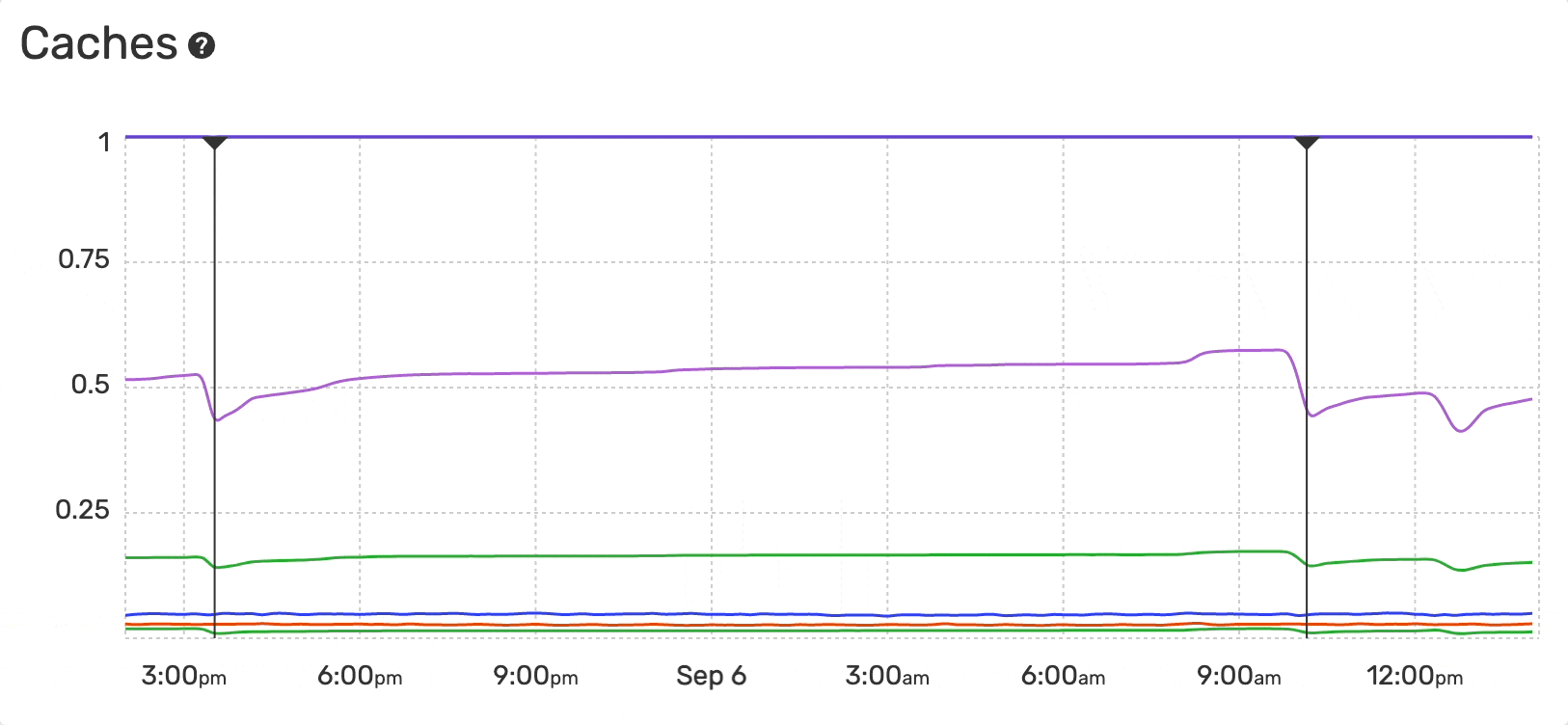
The hit rate is the number of cache hits divided by the total number of memory requests over a given time interval.
The cache usage is the percentage of a specific cache memory currently allocated.
OPcache
¶
OPcache is a PHP extension that improves application performance by storing precompiled script, opcodes, in shared memory. It removes the need to load, parse and compile PHP files on every request.
The opcache.memory_consumption ini setting defines the size of the shared memory storage used by this cache.
OPcache Interned Strings Buffer
¶
Interned strings are a memory optimization added in PHP 5.4. PHP stores
immutable strings (a char *) into a special buffer to be able to reuse its
pointer for all occurrences of the same string.
Blackfire recommends that the interned strings buffer does not represent more than 85% of the allocated memory.
This setting can be adjusted using the opcache.interned_strings_buffer.
OPcache Accelerated Files
¶
The opcache.max_accelerated_files
ini setting configures the maximum number of files that can be cached. Complex
applications involve a lot of different PHP files, so it's recommended to
increase the default value of opcache.max_accelerated_files in production.
RealPath Cache
¶
The realpath() function
returns the absolute path for any given relative file path. This conversion takes
a non-negligible time because it performs some filesystem calls. That's why PHP
caches the results of realpath() calls and their associated
stat() calls. The
realpath_cache_size
ini setting defines the size of this cache.